Can Hearing Loss Be Reversed? When It’s Possible and When It’s Not
Noticing changes in your hearing often raises the question of whether it
By: admin | January 19, 2026
Noticing changes in your hearing often raises the question of whether it will improve on its own or if the changes are more lasting. Hearing loss can have many causes, and how it affects your ear plays a big role in what to expect.
Some types can respond to treatment and show improvement, while others may involve lasting changes that need a different approach to manage. Understanding the nature of your hearing loss helps you know what to expect and allows you to focus on the right treatment for your needs.
Having a clear understanding of your hearing situation helps you make informed decisions about next steps. If improvement is possible, addressing it promptly can make a difference. If the changes are permanent, knowing this early gives you the chance to explore practical ways to maintain or enhance your hearing in daily life.
Consulting with a local hearing specialist provides guidance and clarity, so you can plan your care based on your current needs.
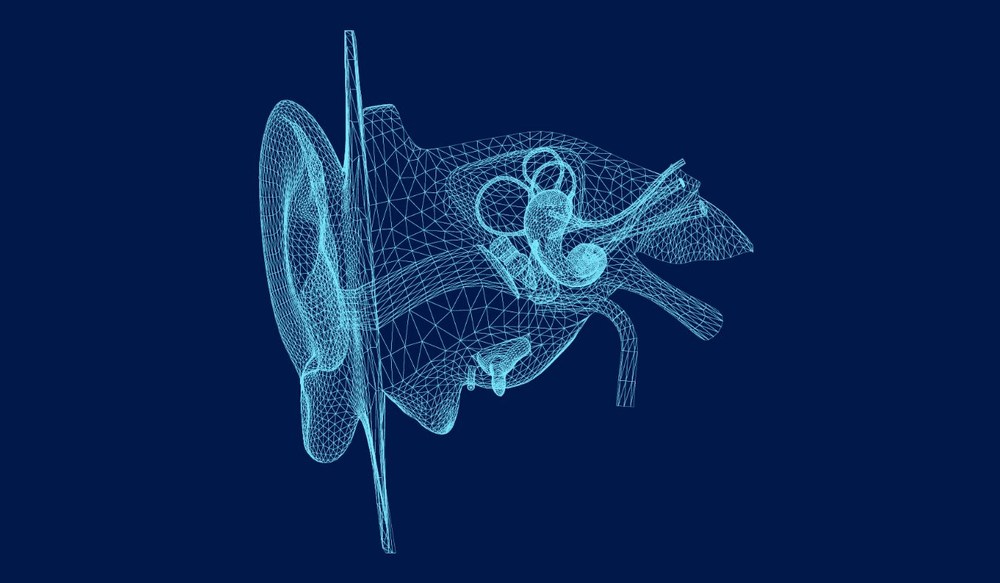
Sound enters your ear as vibrations in the air, which are first collected by the outer ear and directed into the ear canal. These vibrations cause the eardrum to move, and the movement is passed along to the small bones in the middle ear, called the ossicles.
Each of these bones helps transfer and amplify the sound, preparing it to reach the inner ear. This process allows you to pick up a wide range of sounds, from quiet whispers to louder environmental noises.
In the inner ear, the vibrations reach the cochlea, a fluid-filled structure lined with tiny hair cells. These hair cells change the mechanical vibrations into electrical signals that travel through the auditory nerve to the brain.
Your brain interprets these signals, so you recognize what you are hearing, whether it is speech, music or everyday sounds. Understanding this pathway shows why problems at any stage of the ear, from the outer ear to the inner ear, can impact hearing and why protecting your ears is important.
Hearing loss can take several forms, and each type affects your hearing in different ways. Conductive hearing loss happens when sounds have trouble getting through the outer or middle ear to reach the inner ear.
This can make sounds seem quieter or muffled, but the inner ear itself is usually still healthy. Sensorineural hearing loss involves damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve, which can make it difficult to hear certain pitches or understand speech clearly, even if sounds are loud enough.
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both, meaning there may be challenges in how sound travels to the inner ear as well as how the inner ear processes it. Knowing which type of hearing loss is present is key to understanding why certain sounds are harder to hear and what kind of solutions might help.
Each type of hearing loss also carries different implications for treatment and management. Conductive hearing loss can sometimes be treated or improved with medical procedures, while sensorineural loss is usually permanent and often managed with hearing devices. Mixed hearing loss may require a combination of approaches.
Understanding the type of hearing loss you have helps guide decisions about hearing aids, medical interventions or lifestyle adjustments. It also explains why some environments or situations feel more challenging than others, giving you a clearer picture of what to expect and how to maintain better hearing in daily life.
Hearing loss can happen for a variety of reasons, and it affects people in many different ways.
Some causes develop gradually over time, while others may appear suddenly. Certain factors may make people more likely to experience hearing changes, and these can vary from person to person.
Understanding that hearing loss has multiple possible causes helps set the stage for exploring which factors might be relevant to you. Knowing this can guide discussions with a hearing specialist and make it easier to take the right steps to protect or improve your hearing.
Temporary hearing loss often results from short-term issues like earwax buildup, fluid from an ear infection or loud noise exposure. Once the cause is addressed, hearing usually returns to normal. Lasting hearing loss is often due to damage in the inner ear or nerves and does not improve with simple treatment.
Temporary hearing loss may appear suddenly and improve with care. Lasting hearing loss tends to develop slowly and does not get better over time. If you notice ringing in your ears or trouble understanding speech even in quiet settings, these may be signs of more permanent changes.
Knowing whether your hearing loss is temporary or lasting helps you decide on the right steps for care. Your hearing instrument specialist can examine your ears and recommend ways to manage your hearing based on your specific situation.
As you get older, your hearing can change in ways that are often gradual and easy to overlook at first. Natural aging can affect the delicate structures in the inner ear and the nerves that carry sound signals to the brain, which can make it harder to catch certain pitches or follow conversations in noisy environments.
These changes don’t happen the same way for everyone, and the pace of hearing loss can vary widely. Being aware that age can play a role in hearing helps you pay closer attention to subtle shifts and take steps, like regular hearing checkups, to maintain your ability to hear clearly as you get older.
Your family history can influence your chances of developing hearing loss. If relatives have experienced hearing loss, you may be more likely to experience it as well.
While you cannot change your genetics, you can take steps to protect your hearing. Avoid loud noises when possible, use ear protection in noisy environments and schedule regular hearing checks to catch changes early.
Some medications can affect hearing, either temporarily or over the long term. Certain drugs may change how your inner ear functions or how sound signals are processed by the auditory system, which can make sounds seem quieter or harder to distinguish.
In many cases, these effects may improve once the medication is adjusted or stopped, though this depends on the type of medication and how it interacts with your body. Being aware of this connection allows you to discuss potential hearing impacts with your hearing specialist, helping you make informed decisions about your treatment while monitoring your hearing closely.
Earwax helps keep your ears clean and protected. Sometimes, though, too much earwax can build up and block the ear canal. This may cause sounds to seem muffled or make your ear feel full. Some people also notice mild discomfort or ringing in the affected ear.
Earwax buildup is a common cause of temporary hearing loss and usually improves once the extra wax is safely removed by a hearing specialist. Paying attention to changes in your hearing or comfort, especially after cleaning your ears at home, helps keep your ears healthy.
Lasting inner ear damage means that the tiny hair cells or nerves inside your ear have been harmed and cannot repair themselves. This type of damage often leads to permanent hearing loss.
Signs of lasting inner ear damage include:
Hearing devices can provide significant support for people experiencing hearing loss by amplifying sounds and making speech easier to understand. They are designed to target the frequencies where hearing is reduced, helping you pick up on conversations, alarms and everyday sounds that might otherwise be missed.
Modern hearing aids are adjustable, allowing them to be fine-tuned to your specific hearing needs and the environments you spend time in. Using these devices can make daily interactions clearer, whether you are talking with family, attending work meetings or enjoying social activities.
In addition to improving clarity, hearing devices can also reduce the strain on your brain from trying to fill in missing sounds.
When your ears receive a more complete range of sound, it becomes easier to follow speech without constantly guessing what was said. This can make listening less tiring and more natural, allowing you to focus on the conversation itself rather than struggling to hear.
Working with a hearing specialist ensures that your devices are programmed correctly and maintained properly, so they continue to support your hearing in a reliable and consistent way.
Simple habits can help protect your hearing for years to come. Lowering the volume on headphones and taking breaks from loud environments are good places to start.
Wearing ear protection like earplugs or earmuffs is important if you spend time around loud machinery, concerts or sporting events. Staying active and eating a balanced diet support healthy blood flow to the ears.
Managing health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure is also important for hearing health since these conditions affect blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the ears. Regular checkups help spot issues early and support both overall wellness and long-term hearing.
If you often ask people to repeat themselves or have trouble following conversations, it may be time to visit a hearing specialist. Difficulty hearing clearly in group settings or noisy places can also signal changes in your hearing.
Turning up the volume on devices higher than before or feeling like others are mumbling are other common signs. Noting when these changes happen can help you share clear information during your appointment.
Whether hearing loss can be reversed depends on its cause and type. Some forms, like those from earwax buildup or certain infections, may improve with treatment.
Others linked to lasting inner ear damage or genetics are usually permanent but can often be managed with the right tools and support. Recognizing these differences helps you make choices that fit your needs and lifestyle.
If you have noticed changes in your hearing or want to learn more about your options for care, our team is here to help. A full hearing check at can provide answers about your type of hearing loss and what steps might work best for you.
For more information or to schedule an appointment, you can reach out to Hearing Center of Columbia in Columbia, TN at (931) 548-1166. Taking action now can help you maintain your quality of life and stay connected with those around you.
Tags: hearing loss and mental health, hearing loss symptoms, types of hearing loss

Noticing changes in your hearing often raises the question of whether it
By: admin | January 19, 2026

Exercise benefits your body in ways that extend beyond muscle strength and
By: admin | November 18, 2025
When hearing difficulties begin, it can feel challenging to adjust to the
By: admin | September 24, 2025
